|
Oreilly, October 27, 2004 How to Use JMS with PHP |
||
| JMS (Java Messaging Service) is an interface implemented by most J2EE containers in order to provide point-to-point queuing and topic-based (publish/subscribe) functionality. JMS is frequently used by enterprise and back-end applications for distributed communication and collaboration. PHP is a powerful scripting language popular for use with Apache's CGI facility.
|
||
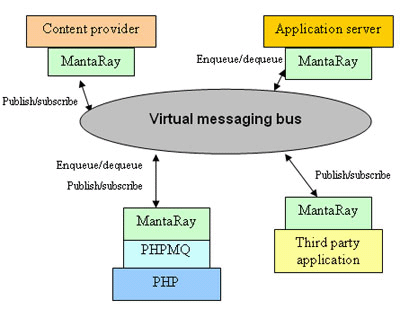
JMS (Java Messaging Service) is an interface implemented by most J2EE containers in order to provide point-to-point queuing and topic-based (publish/subscribe) functionality. JMS is frequently used by enterprise and back-end applications for distributed communication and collaboration. PHP is a powerful scripting language popular for use with Apache's CGI facility. Although efforts are being made to develop PHP as a back-end scripting language, its use is still very much confined to front-end applications. Combining the strengths of PHP--easy and fast web development, and compatibility with many types of databases--with those of JMS, which is the standard for communication with back-end enterprise applications, creates a powerful and easy-to-use tool for both Java and PHP developers. PHPMQ gives the PHP developer JMS-like abilities through the MantaRay messaging bus. This document gives an overview of PHPMQ and its use by the PHP developer. DefinitionsMantaRay: MantaRay is an open source, serverless transport layer designed specifically for heterogeneous, distributed, and high-traffic environments. It has a JMS API (1.1 and 1.02) as well as RMI, HTTP, and proprietary APIs. Compared to traditional messaging systems, such as busses or brokers, MantaRay provides a much higher level of robustness, better performance, and faster implementation by eliminating the need for a broker and bringing all functionality to the edges. MantaRay eliminates the single point of congestion and single point of failure of traditional models by using a peer-to-peer, serverless architecture. The distributed application is lightweight and agnostic to the operating system. PHPMQ: PHPMQ is an open source serverless messaging toolkit for PHP, giving the PHP developer the ability to perform JMS operations such as sending and receiving messages on queues and topics while ensuring delivery and enabling persistent messaging. PHP/JAVA integration: PHPMQ uses the PHP/Java integration extension of PHP. The Java extension provides a simple and effective means for creating and invoking methods on Java objects from within PHP. The JVM is created using JNI, and both the PHP script and the JVM run inside of the PHP process. The PHP/Java integration is used to connect to the messaging bus via Remote Method Invocation (RMI); the PHPMQ Java client performs a lookup and retrieves the MantaRay RMI API, and messaging operations like enqueue and dequeue are performed on that API. PHP in the World of MessagingWith PHPMQ, developers get the ability to communicate with other applications on the message bus, whether they are written in PHP, Java, or C++, using standard JMS-like messaging: enqueuing messages to queues and dequeuing them, and publishing messages to topics and subscribing for them. Figure 1 show how PHP scripts connect to the world of messaging with PHPMQ.
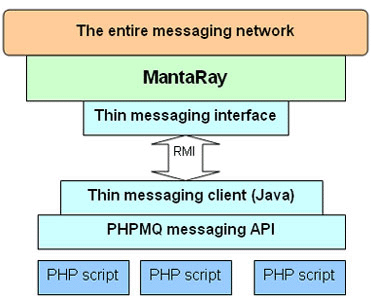
PHPMQ runs a thin Java client that connects to the message bus and is the incoming and outgoing interface of the bus. The client uses the RMI API to communicate with a messaging interface located on the message bus. The interface exposes the messaging abilities of MantaRay and maintains a stateful session for the remote (PHP) client, in order to keep the PHP client as thin as possible, and to provide a long-lived messaging session despite using a short-lived script. Figure 2 show the communication layers between the PHP script and the MantaRay message bus.
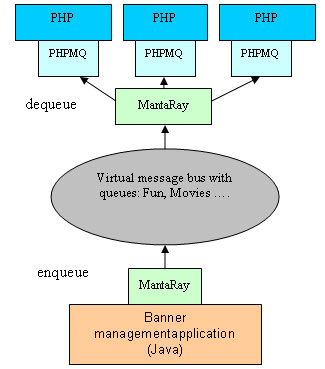
An Example of a PHPMQ-Powered ApplicationThe "Smart Banners" Example ApplicationBanners are advertisements added to an HTML page. They usually appear at the top of the page. Suppose we have a banner management application written in Java. This application decides which banners should be displayed and at what frequency the banners should be changed. The Java application also categorizes these banners into subjects such as finance, entertainment, movies, etc. The Java application enqueues the URLs of the banner to queues named Finance, Entertainment, Movies, etc. On the other side of the messaging bus is a PHP script whose role is to add the banner according to knowledge about the viewing user (e.g., if the user is a member of a finance forum, them the PHP should display a finance-related banner). The PHP script dequeues URLs from the appropriate queue(s) and displays the banners at the top of the HTML page. Figure 3 shows the components in the "smart banners" example.
The management application code might look something like this: The PHP code might look something like this: The "smart banner" separates the application into two tiers, a logic tier that manages the banners and enqueues them (Java), and a presentation tier that dequeues the banners from the queues based on user information (PHP). How to Install and Configure PHPMQThis section describes how to install and configure all of the components so that PHP scripts will run under PHPMQ. Step 1. Installing and Configuring the MantaRay Message LayerDownload and unzip the MantaRay messaging layer. Enable the RMI API in the MantaRay configuration:
There are security considerations that need to be taken into account in order for the RMI API to work. Refer tojGuru: Remote Method Invocation: Introduction, and the security policy at Tom Valesky's "How to Create an RMI System." Step 2. Installing and Configuring PHP
Most PHP scripts run over Apache and enable a dynamic user interface with an HTTP browser. Step 3. Running the MantaRay LayerStart MantaRay by running Step 4. Running the PHP Script and Creating an Instance of the Messaging APITo create an instance of the PHP messaging API, a PHP script should include messaging.php, like this: The parameters passed at instantiation are the host name and port number of the MantaRay RMI Registry. Step 5. Using the PHPMQ Messaging APIAfter an instance of the messaging API has been created, developers can start working with the functions provided by the messaging API. These functions are discussed in the next section. Messaging API FunctionsThe PHPMQ messaging API includes the following functions:
In the PHPMQ download package, there are several example applications that use both queues and topics. ConclusionThe ability of languages to cooperate is very important, but in many cases is still lacking or hard to implement. As a community, we should strive to always use the right tool for the task and ensure that these tools communicate with each other seamlessly. PHPMQ is an example of how two languages can empower each other: using PHPMQ gives the PHP developer a window to the back-end world and gives the Java developer the freedom to use an easy and fast web development tool as his front-end tier (instead of the JSP/servlet approach that is more difficult to work with). With PHPMQ, you can have a long-lived Java application maintaining a session and keeping persistent data for the short-lived PHP scripts. Related Links
Amir Shevatis a senior software developer with eight years of experience in computing. |

| Designed by Intellity Interactive Media | ©2002 Israel Seed Partners | Webmaster |